Aalternative ccriteria oof nnormality to the editor.
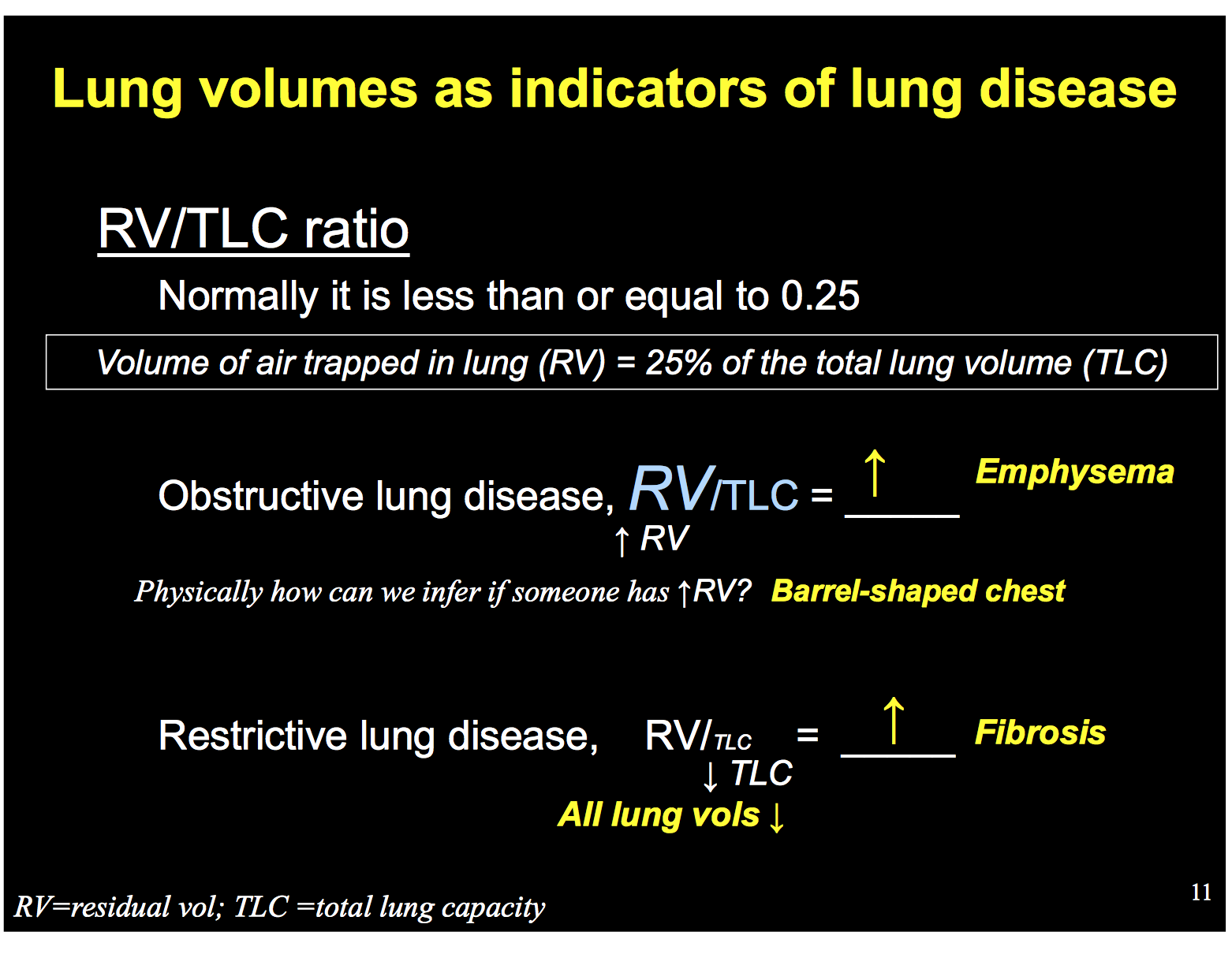
Rv tlc ratio emphysema.
Mild 60 70 di t d d t70 predicted.
Diseases which lead to a reduction in inward recoil of the lung emphysema result in an increase in tlc known as hyperinflation.
While the criteria used to diagnose airway obstruction using fev1 fvc ratio and assess its severity using fev1 are uniformly recognized 5 35 the presence and severity of gas trapping and static hyperinflation can be described using a plurality of indices the most common being residual volume rv functional residual capacity frc total lung capacity tlc rv tlc ratio and frc tlc.
The accuracy of this criterion has been questioned.
Moderately severe 50 predicted.
In a retrospective analysis we observed that abnormal rv tlc ratio was a better predictor for obstruction.
Although the european respiratory society ers proposes using percentiles or standardized residuals for reporting results of lung volume measurements 1 this approach has not been widely accepted and percentages are still being used mainly because calculations and in.
In each study age is the main coefficient describing the relationship between rv and tlc see text.
Rv tlc ratio normal range.
Obstructive lung diseases particularly emphysema result in an increase in the rv and rv to tlc ratio.
In severe emphysema particularly bullous emphysema the tlc can show a marked increase.
35 or predicted rv tlc 35 or predicted indicates air trapping.
Ratio of residual volume rv to total lung capacity tlc plotted as a function of age for authors of white predicted sets in which the ratio was reported.
Elevated rv and rv tlc ratio suggest air trapping with obstructive lung disease.
Rv tlc expressed as a percent is plotted against the predicted fev 1 for 4 774 patients with asthma or copd with solid lines representing the best fit for each.
Tlc 80 restrictive disease ats criteria for severity.
Residual volume rv to total lung capacity tlc ratio versus fev 1 predicted.
Severe step 5.
Keep it simple 70 80 predicted.